According to a Nov. 26, 2019 Boston GLOBE editorial, there are four tasks necessary to ease the housing crisis in the Greater Boston Region:
By Luc Schuster, CommonWealth Magazine, 11/16/19
Does Arlington need more housing? If yes, will more housing result in higher school costs? There is a perception that more housing means more school age children and more school age children will strain the capacity and expand the budget of the Arlington Public Schools.
A recently constructed project with 44 units of affordable housing shares a footprint with a new public library in this Chicago neighborhood. The Mayor and the Housing Authority initiated a competition for proposals from architecture firms to build projects that feature the “co-location” of uses, “shared spaces that bring communities together”, according to a recent article by Josephine Minutillo in ARCHITECTURAL RECORD (October 2019).
Like numerous metro areas in the United States, Greater Boston has both a shortage of housing and high housing costs. According to a recent presentation by Town Manager Adam Chapdelaine, Boston and the immediate surrounding communities added new 148,000 jobs and 110,000 new residents in the period 2010–2017. But despite the increase in jobs and population, we’ve only permitted 32,500 new homes.
The material in this post came from my efforts to learn about when Arlington’s housing was built. The data comes from the town’s 2019 property tax assessments, where I took our nineteen-thousand-and-some-odd homes and apartments and broke them down by housing type and decade built. It’s not exactly a history housing of production, though it is a close approximation. In this analysis, a single-family home built in the 1912 and rebuilt as a two-family in 1976 would show up as two units built in the 1970s. Similarly, a three-family home that was built in the 1924 and later converted to condominiums would show up as three condominiums built in the 1920s.
Prepared by: Barbara Thornton with the capable assistance of Alex Bagnall, Pamela Hallett, Patrick Hanlon, Karen Kelleher, Steve Revilak and Jennifer Susse.
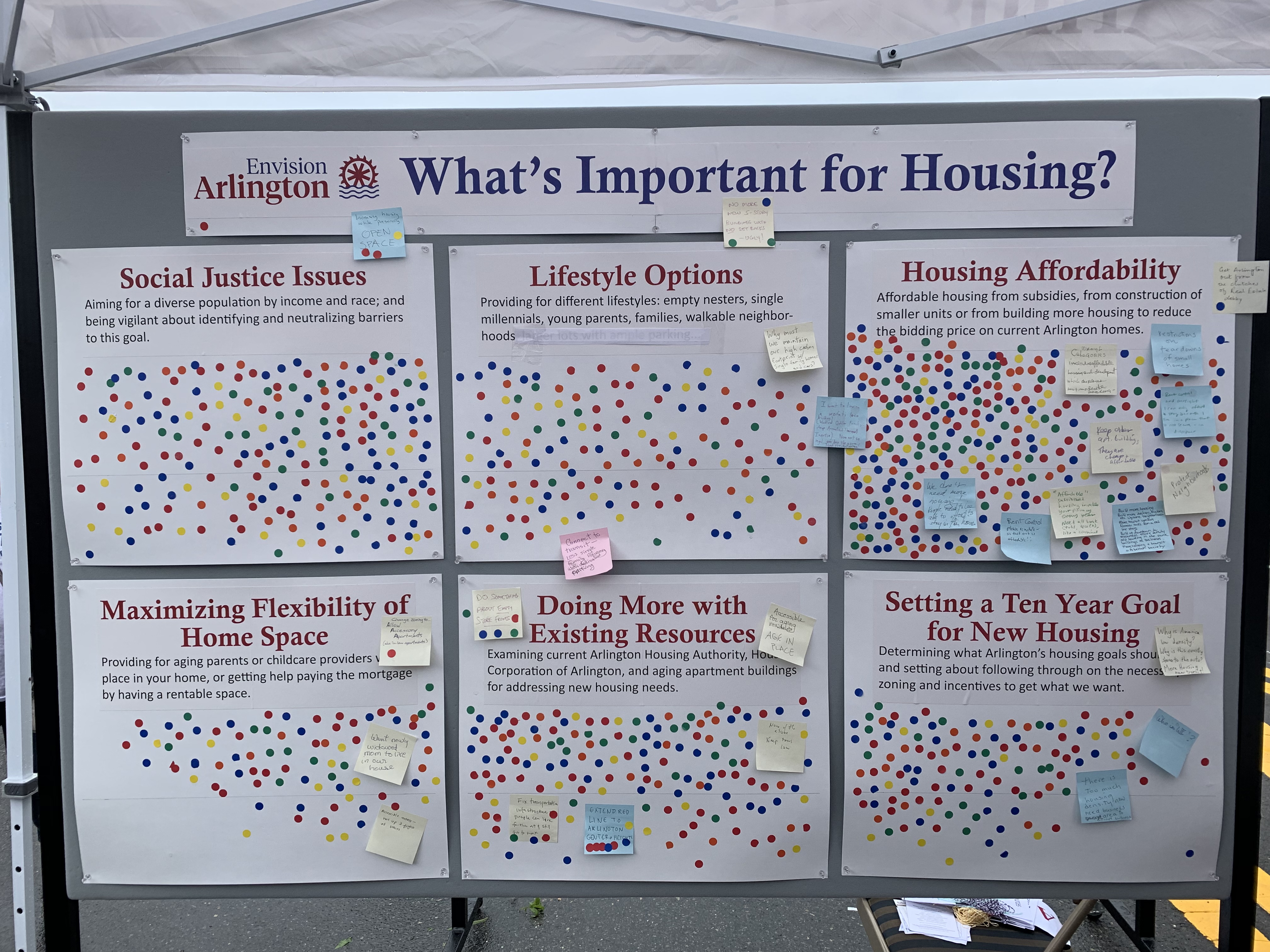
A portion of Envision Arlington’s town day booth was designed to spark a community conversation about housing. Envision set up a display with six poster boards, each representing a housing-related topic. Participants were given three dots and asked to place them on the topics they felt were most important. There were also pens and post-it notes on hand to capture additional comments. This post is a summary of the results. You could think of it as a straw-poll or temperature check on the opinions of town day attendees.
The City of Somerville estimates that a 2% real estate transfer fee — with 1% paid by sellers and 1% paid by buyers, and that exempts owner-occupants (defined as persons residing in the property for at least two years) — could generate up to $6 million per year for affordable housing. The hotter the market, and the greater the number of property transactions, the more such a fee would generate.
According to Richard Rothstein in his 2017 book, Color of Law: A Forgotten History of How Our Government Segregated America, “we have created a caste system in this country, with African-Americans kept exploited and geographically separate by racially explicit government policies,” he writes. “Although most of these policies are now off the books, they have never been remedied and their effects endure.” Zoning was one of the policies that contributed significantly to this outcome.