If subsidization proposals return to Boston and Massachusetts again next year, they will not be a silver bullet for affordability, but could be one ingredient in a successful strategy alongside more housing construction.
A new report for Boston Indicators, “Exclusionary by Design”, shows the clear intent of many Greater Boston suburbs to resist racial and class integration in the 1970s. Housing scholar Amy Dain demonstrates how racial prejudice and class exclusion figured into suburbs’ downzoning in the 1970s; and how putatively legitimate concerns like tax revenue, aesthetic continuity, and the environment served the cause of exclusion.
An ADU is a separate, smaller living unit with its own kitchen and bathroom facilities and separate entrance that is included within a larger resident (type 1), attached to a residence (type 2) or located in an accessory (“detached”) structure on the same lot as a main residence (type 3). For a variety of reasons, primarily cost and feasibility, the type 1 ADUs are by far the most common.
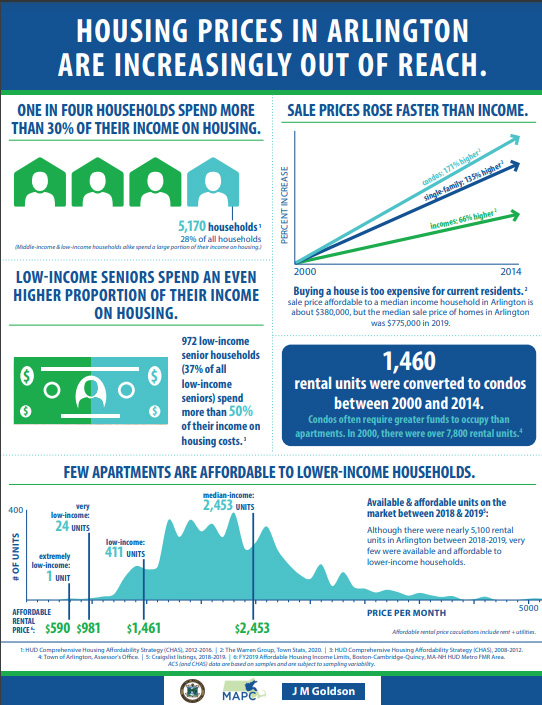
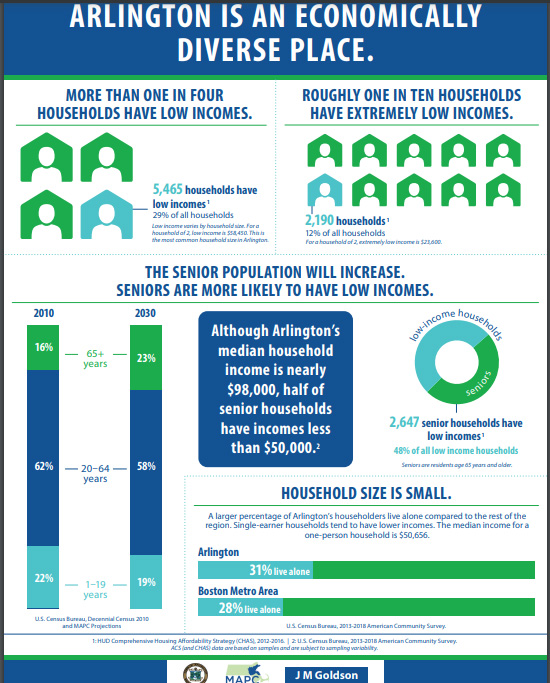
Beginning last July, 2020, the Town of Arlington and community groups in the town are sponsoring a number of webinars and zoom conversations addressing the need for affordable housing programs in Arlington. Several factors contribute to the Arlington housing situation: diversity of housing types, prices, diversity of incomes, availability of housing subsidies, rapid growth in property values that greatly exceed the rate of growth of income.
This is our national challenge for the next 25 years, according to Jeffrey C. Fuhrer, Executive Vice President/Chief Strategy Officer for MassDevelopment, the Commonwealth’s economic development and finance authority.
Accessory Dwelling Units (aka “granny flats”)
Arlington has an opportunity to set up an Affordable Housing Trust Fund to provide more housing stability for its low and moderate income residents. The vote will occur in the Town Meeting starting Nov. 16, 2020.
A Guide for Arlington
The Massachusetts Housing Partnership put together this 2018 guidebook, v.3, to help municipalities adopt Municipal Affordable Housing Trust Fund (MAHT) legislation to suit the specific needs of each municipality.
For Arlington’s Nov 2020 Special Town Meeting, my colleague Ben Rudick filed the following warrant article:
