Restrictive covenants are a “list of obligations that purchasers of property must assume … For the first half of the 20th century, one commonplace commitment was a promise never to sell or rent to an African American”. [1] These covenants gained popularity after the Supreme Court’s 1917 decision in Buchanan v. Warley.
In the 1930’s the Home Owner’s Loan Corporation of America (HOLC) created actuarial maps of the United states. These maps were color coded — Green, Blue, Yellow, and Red — to reflect the amount of “risk” associated with home loans in those areas. The colors corresponded to “Best” (green), “Still Desirable” (blue), “Definitely Declining” (yellow), and “Hazardous” (red). Being in a green area made you likely to secure a federally-insured home mortgage, something that was effectively unavailable to red areas. Red areas were often associated with black populations, and these maps are where the term “redlining” comes from.
I live on Sunnyside Avenue in Arlington, Massachusetts. The neighborhood was built as two subdivisions in 1948, with 42 duplexes (84 homes total). These were starter homes with 792 square feet of finished space plus a basement with a garage. I affectionately refer to them as excellent specimens of mid-century slap-up. They were constructed in the mid 20th century, and the builder just kind of slapped them up.
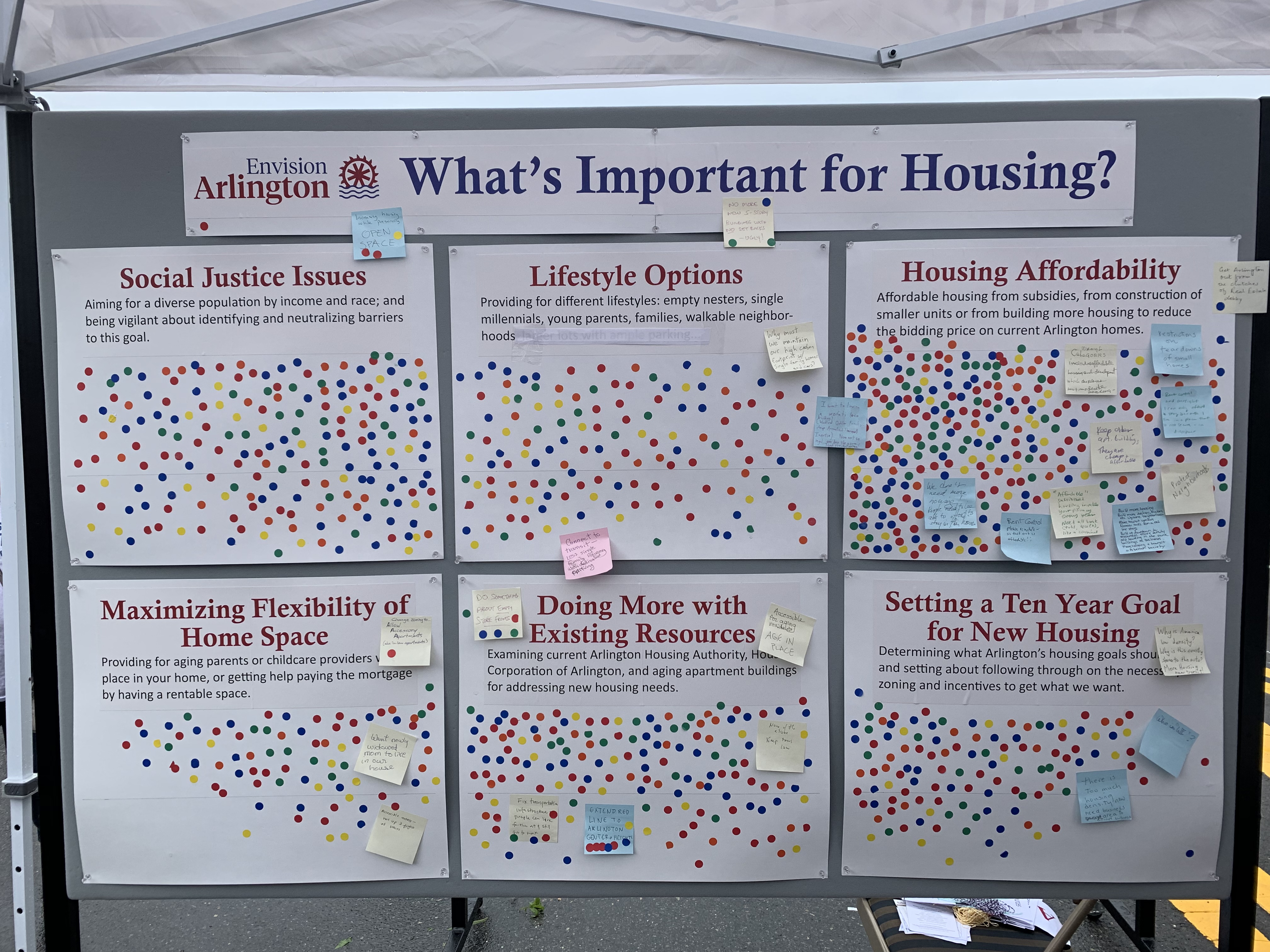
A portion of Envision Arlington’s town day booth was designed to spark a community conversation about housing. Envision set up a display with six poster boards, each representing a housing-related topic. Participants were given three dots and asked to place them on the topics they felt were most important. There were also pens and post-it notes on hand to capture additional comments. This post is a summary of the results. You could think of it as a straw-poll or temperature check on the opinions of town day attendees.
According to Richard Rothstein in his 2017 book, Color of Law: A Forgotten History of How Our Government Segregated America, “we have created a caste system in this country, with African-Americans kept exploited and geographically separate by racially explicit government policies,” he writes. “Although most of these policies are now off the books, they have never been remedied and their effects endure.” Zoning was one of the policies that contributed significantly to this outcome.
This infographic demonstrates in data and graphs why Arlington needs more housing.
by Alexander vonHoffman, Joint Center for Housing Studies, Harvard University, February 2006
Issues of supply, affordability, and equity all contribute to an ongoing housing crisis in Massachusetts. Among U.S. metro areas with knowledge-based industries, metro Boston ranks near the bottom in housing production and near the top on development costs. Due to the latter, production of new affordable housing units has scarcely increased over the past decade. And largely decentralized authority over land use regulations, by 351 cities and towns, does little to foster uniform housing equity standards.