This 102 page document is the most recently revised set of recommendations by the Town of Arlington’s Redevelopment Board. The report takes into consideration the comments and information provided over the last few months’ public hearing process. It also incorporates a citizen petition which strengthens the case for increasing permanent affordable housing with the passage of these zoning related Articles. Town Meeting convenes on April 22, 2019.
Related articles
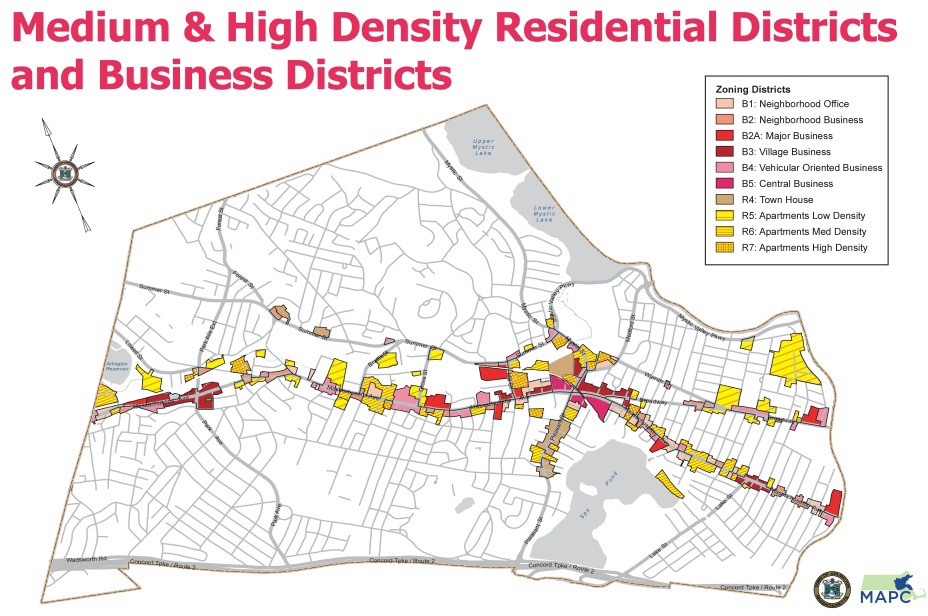
The discussions on zoning have been confusing because while zoning covers ALL of Arlington’s land and the zoning bylaws for all Arlington’s zones are referenced, the key issues of greatest interest to Town Meeting are the discussions about increasing density. These discussions pertain ONLY to those properties currently zoned as R4-R7 and the B (Business) districts. These density related changes would affect only about 7% of Arlington’s land area. The map shows the specific zones that would potentially be affected. They lay along major transportation corridors.
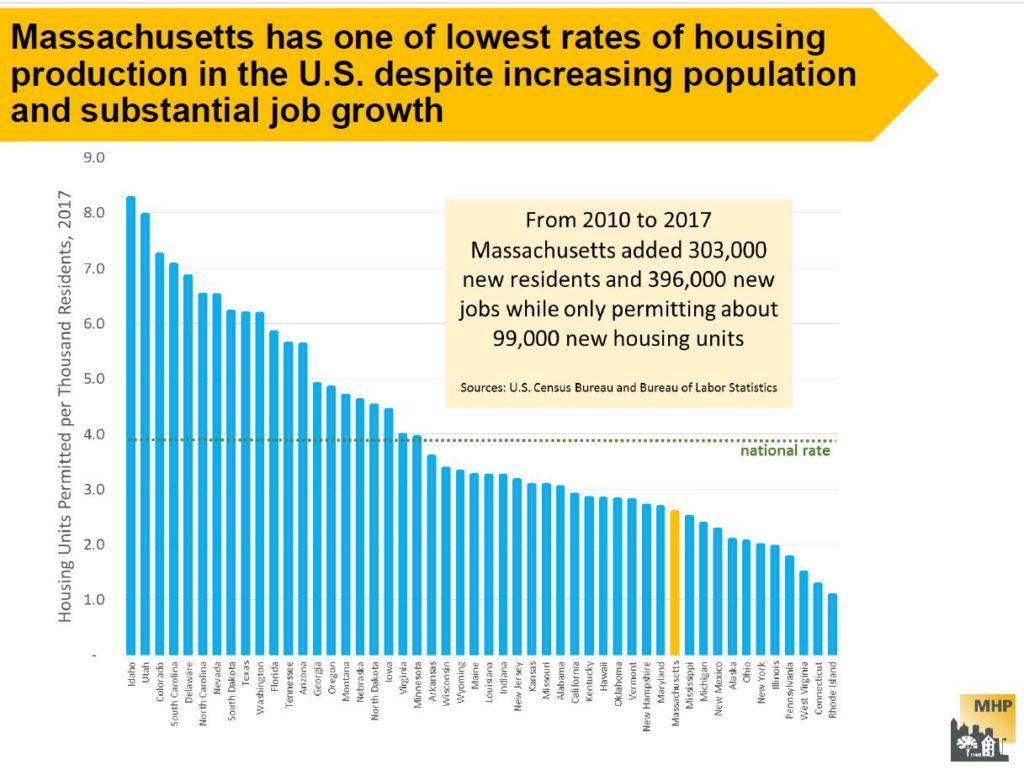
Data in a Mass Housing Partnership report shows how far behind the Boston metropolitan area has fallen in meeting the housing needs of its citizens. There are four primary categories for measuring the inadequacies: 1. Availability, 2. Affordability, 3. L0cation and Mobility and 4. Equitability. See the full report for more data and examples. Two slides are shown below.
The calculation for what is permanently affordable housing is complicated. Arlington’s affordable rate is based on a region that includes the Area Median Income (AMI) of the Cambridge-Boston-Quincy region. The rate is adjusted and reset periodically according to federal HUD guidelines. The rate is applied based on family size and on the Town’s definition of what income level is eligible for Inclusionary Housing opportunities in Arlington. In Arlington a 3 person family would qualify if their income was under 60% of AMI. At this time, that is approximately $58,000 for a family of three.
For more information, see this table of income limits from Cambridge’s Community Development Department, and this short paper on affordable housing from the City of Boston.
It’s January 2023, and as we do every year, folks in Arlington are taking out nomination papers, gathering signatures, and strategizing on how to campaign for the town election on Saturday April 1st. The town election is where we choose members of Arlington’s governing institutions, including the Select Board (Arlington’s executive branch), the School Committee, and — most relevantly for this post — Town Meeting.
If you’re new to New England, Town Meeting is an institution you may not have heard of, but it’s basically the town’s Legislative Branch. Town Meeting consists of 12 members from each of 21 Precincts, for 252 members total. Members serve three-year terms, with one-third of the seats up for election in any year, so that each precinct elects four representatives per year (perhaps with an extra seat or two, as needed to fill vacancies). For a deeper dive, Envision Arlington’s ABC’s of Arlington Government gives a great overview of Arlington’s government structure.
As our legislative branch, town meeting’s powers and responsibilities include:
- Passing the Town’s Operating Budget, which details planned expenses for the next year.
- Approving the town’s Capital Budget, which includes vehicle and equipment purchases, playgrounds, and town facilities.
- Bylaw changes. Town meeting is the only body that can amend the towns bylaws, including ones that affect housing and commercial development.
Town Meeting is an excellent opportunity to serve your community, and to learn about how Arlington and its municipal government works. Any registered voter is eligible to run. If this sounds like an interesting prospect, I’d encourage you to run as a candidate. Here’s what you’ll need to do:
- Have a look at the town’s Information for new and Prospective Town Meeting Members.
- Contact the Town Clerk’s office to get a set of nomination papers. You’ll need to do this by 5:00 PM February 8th, 2023 at the latest.
- Gather signatures. You’ll need signatures from at least ten registered voters in your precinct to get on the ballot (it’s always good to get a few extra signatures, to be safe).
- Return your signed nomination papers to the Clerk’s office by February 10, 2023 at noon.
- Campaign! Get a map and voter list for your precinct, knock on doors, and introduce yourself. (Having a flier to distribute is also helpful.)
- Vote on Saturday April 1st, and wait for the results.
Town Meeting traditionally meets every Monday and Wednesday, from 8:00 — 11:00 pm, starting on the 4th Monday in April (which is April 24th this year), and lasting until the year’s business is concluded (typically a few weeks).
If you’d like to connect with an experienced Town Meeting Member about the logistics of campaigning, or the reality of serving at Town Meeting, please email info(AT)equitable-arlington.org and I’d be happy to make an introduction.
During the past few years, Town Meeting was our pathway to legalizing accessory dwelling units, reducing minimum parking requirements, and loosening restrictions on mixed-use development in Arlington’s business districts. Aside from being a rewarding experience, it’s a way to make a difference!
Two weeks ago, I helped to organize a precinct meeting for residents and town meeting members. During the meeting, we got into a discussion about public open spaces, how the town funds their upkeep, and whether having more commercial tax revenue might provide additional funding for parks and recreation.
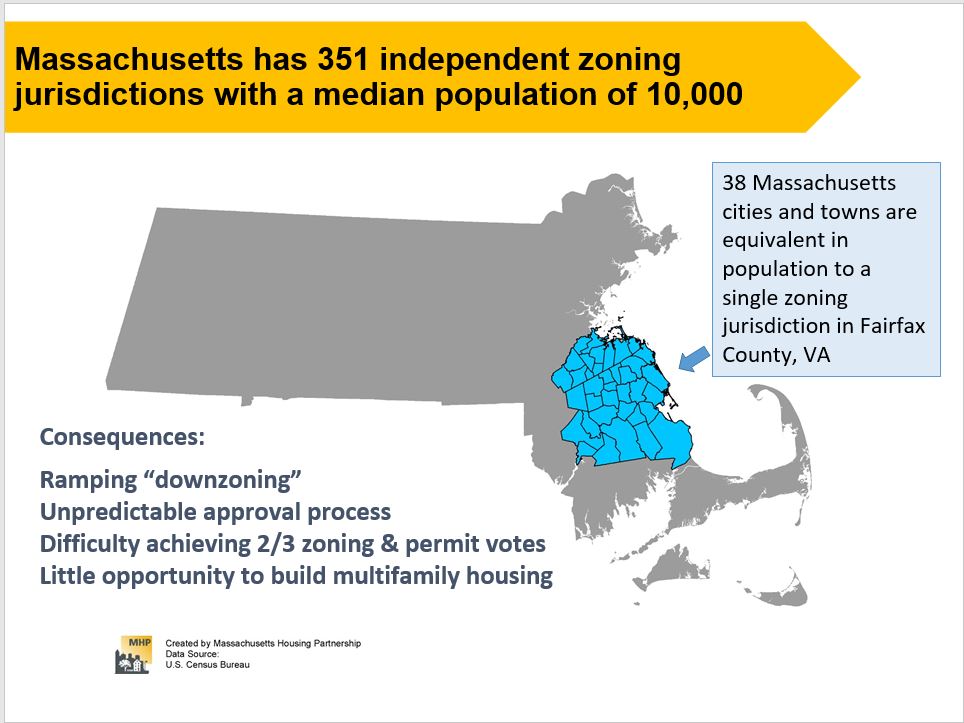
As I discussed in an earlier post, only about 5.6% of Arlington’s is zoned for commercial uses, and that limits the amount of commercial property tax revenue we can generate. Commercial property tax revenue is sometimes referred to as “CIP”, which stands for “Commercial, Industrial, and Personal”. Commercial and Industrial refer to property taxes on land and buildings that are respectively used for commercial and industrial uses. Personal tax is tax on the value of equipment that’s owned and used by a business for the purpose of carrying out whatever their business is. This could include things like desks, display fixtures, cooking equipment, fork lifts, and the like.
In 2020, Arlington’s CIP levy was 5.45%, meaning that 5.45% of our property tax revenue came from Commercial, Industrial, and Property tax revenue. Breaking this down further, 4.2% was commercial ($5,562,528 tax levy), 0.2% was industrial ($278,351 tax levy), and 1.1% was personal ($1,423,117 tax levy). The town’s total 2020 tax levy was $133,350,155. This data comes from MassDOR’s Division of Local Services, and I’ll provide more specific sources in the “References” section of this post.
A CIP levy of 5.45% is low (compared with other communities in the commonwealth), and occassionaly folks like to talk talk about how to raise it. Which is to say, we about how to raise the ratio of commercial to residential taxes. I moved to Arlington in 2007, when our CIP levy was 5.37%. This increased in subsequent years, peaking at 6.26% in 2013, and has been gradually decreasing since. Recall that 2008 was the year the housing market crashed, and the “great recession” began. The value of Arlington’s residential property fell, but the value of business properties was relatively stable in comparison. Thus, our CIP percentage got a boost for a couple of years.
Tax levies (the amount of tax collected) are a direct reflection of the tax basis (the assessed value of property). I’m going to shift from talking about the former to talking about the latter, because that will lead nicely to a discussion about property wealth. Which is to say, the aggregate value of property assessments in town.
Here’s a chart showing Arlington’s net CIP and residential property values, from 1983–2020, adjusted to 2020 dollars. (This is similar to the chart that appears on page 102 of Arlington’s Master plan, but for a longer period of time).
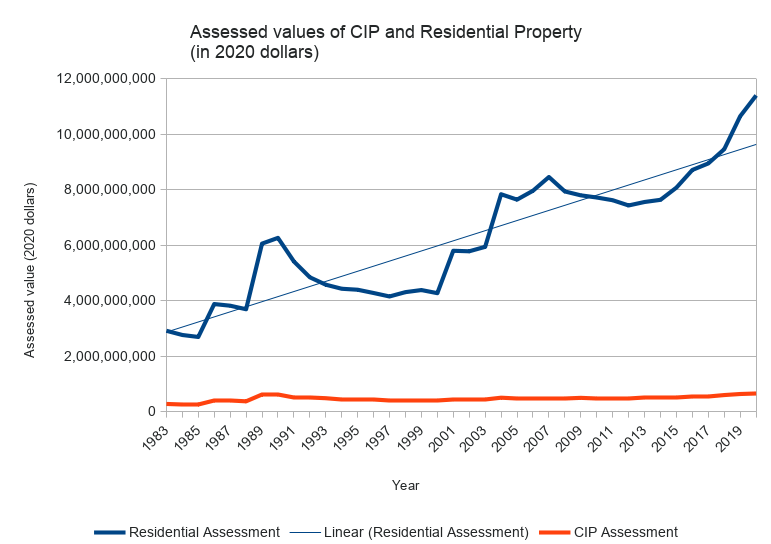
Generally speaking, the value of Arlington’s residential property has appreciated considerably, and there’s a widening gap between our residential and CIP assessments (in terms of raw dollars). Because the gap is so large, it’s helpful to see it on a log scale.
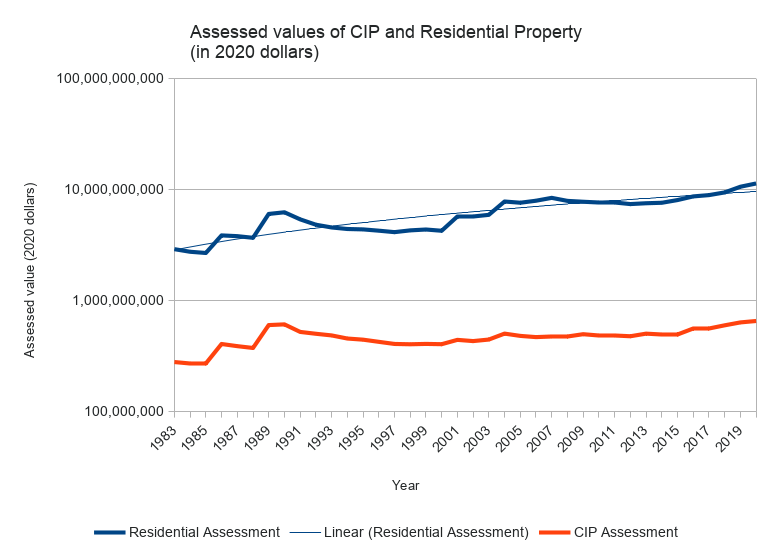
Viewed this way, the curvatures are generally similar, but residential property wealth is rising faster than business property wealth.
In summary, there are three reasons why our CIP is as low as it is: (1) a limited amount of land where one can run a business, (2) the value of residential property is appreciating faster than the value of business property, and (3) occasionally business properties are converted to residential (perhaps with the residential property being worth more than the former business property). That’s not to say we can’t improve the commercial tax base. We can, but we will have to think about what and where, and how to compete with a generally competitive residential market.
References
- MassDOR Division of Local Services reports
- DOR Query Tool for Municipal Property Assessments
- DOR Query Tool for Municipal Tax Levies
- Spreadsheet of Arlington Property Assessments, 1983–2020. Data obtained from MassDOR, with calculations added to adjust for inflation.
- Spreadsheet of Massachusetts Property assessments for 2020. Data obtained from MassDOR.
(Updated 7/2/2020, to add log scale graph and revise conclusion.)
The City of Somerville estimates that a 2% real estate transfer fee — with 1% paid by sellers and 1% paid by buyers, and that exempts owner-occupants (defined as persons residing in the property for at least two years) — could generate up to $6 million per year for affordable housing. The hotter the market, and the greater the number of property transactions, the more such a fee would generate.
Other municipalities are also looking at this legislation but need “home rule” permission, one municipality at a time, from the state to enact it locally. Or, alternatively, legislation could be passed at the state level to allow all municipalities to opt into such a program and design their own terms. This would be much like the well regarded Community Preservation Act (CPA) program that provides funds for local governments to do historic preservation, conservation, etc.
This memorandum from the City of Somerville to the legislature provides a great deal of information on the history, background and justification for such legislation.
House bill 1769, filed January, 2019, is an “Act supporting affordable housing with a local option for a fee to be applied to certain real estate transactions“.
COMMENT:
KK: This article suggests Arlington may be likely to pass a real estate transfer tax: https://www.counterpunch.org/2019/12/19/boston-one-step-closer-to-a-luxury-real-estate-transfer-tax/
The presentation, dated March 11, 2019, includes slides used to present the information necessary to understand the rationale for zoning changes, the location of the zoning areas under consideration and the charts, tables and maps that help describe the situation. The proposed zoning changes, especially articles 6, 7, 8, 11 and 16, only cover changes affecting about 7% of the Town, those parts of the Town that are currently zoned R4-R7 and the B zoning districts.
This timely report on the question of affordable housing vs. density comes from the California Dept. of Housing & Community Development and mirrors the situation in the region surrounding Arlington MA.
Housing production has not kept up with job and household growth. The location and type of new housing does not meet the needs of many new house- holds. As a result, only one in five households can afford a typical home, overcrowding doubled in the 1990’s, and too many households pay more than they can afford for their housing.
Myth #1
High-density housing is affordable housing; affordable
housing is high-density housing.
Fact #1
Not all high density housing is affordable to low-income families.
Myth #2
High-density and affordable housing will cause too much traffic.
Fact #2
People who live in affordable housing own fewer cars and
drive less.
Myth #3
High-density development strains public services and
infrastructure.
Fact #3
Compact development offers greater efficiency in use of
public services and infrastructure.
Myth #4
People who live in high-density and affordable housing
won’t fit into my neighborhood.
Fact #4
People who need affordable housing already live and work
in your community.
Myth #5
Affordable housing reduces property values.
Fact #5
No study in California has ever shown that affordable
housing developments reduce property values.
Myth #6
Residents of affordable housing move too often to be stable
community members.
Fact #6
When rents are guaranteed to remain stable, tenants
move less often.
Myth #7
High-density and affordable housing undermine community
character.
Fact #7
New affordable and high-density housing can always be
designed to fit into existing communities.
Myth #8
High-density and affordable housing increase crime.
Fact #8
The design and use of public spaces has a far more
significant affect on crime than density or income levels.
See an example of a “case study” of two affordable housing developments in Irvine CA, San Marcos at 64 units per acre.

San Paulo at 25 units per acre.

Both are designed to blend with nearby homes.
