In 2015 Town Meeting approved the Master Plan. Following is the Housing chapter of that plan. It contains a great deal of information about details of the housing situation in Arlington, challenges of housing price increases, needs for specialty housing, opportunities for meeting these needs, etc. The authors found that “most cities and towns around Arlington experienced a significant rise in housing values from 2000 to 2010. A 40 percent increase in the median value was fairly common. However, Arlington experienced more dramatic growth in housing values than any community in the immediate area, except Somerville. In fact, Arlington’s home values almost doubled.” This and related data helps explain why the need for affordable housing is now so acute.
Related articles
This is the second in a series of “Arlington 2020” articles. The first article looked at the number of one-, two-, and three-family homes and condominiums in Arlington, and how that housing stock has changed over time. This article will examine changes in the value of those properties. We’re going to look at “value” through the lens of property assessments, so we should start with an explanation of what property assessments are and how they’re used.
A property assessment is simply the Town Assessor’s best estimate of what a property is worth, based on market values. The assessor’s office inspects properties every ten years; during intervening years, assessments are adjusted based on sale prices of similar homes in a given tax neighborhood. For all practical purposes, assessed values tend to trail market values by two years. In my neighborhood, property assessments are spot on — my house was assessed at $501,000 in 2020; during 2018, sales of similar homes in the neighborhood ranged from $495,000 to $520,000.
Condominiums have a single assessed value, which includes land and buildings. Otherwise, assessed values are broken down into land value, building value, and yard items (e.g., a garage or a shed).
Assessed values are used to determine the tax rate. The assessors page on the town website has calculations in worksheet form, but for all practical purposes, it’s just a division problem. One takes the total tax levy and divides by the sum of all property assessments (in thousands of dollars), and that’s the tax rate. An individual’s taxes are the assessed value of their property (in thousands of dollars) multiplied by the tax rate. If an individual owns (say) 1% of the assessed value in town, that individual will pay 1% of the property tax levy.
The main point is that assessed values are based on market values, but with a two-year lag. Consequently, we can use them as a way to see how home prices have changed over time.
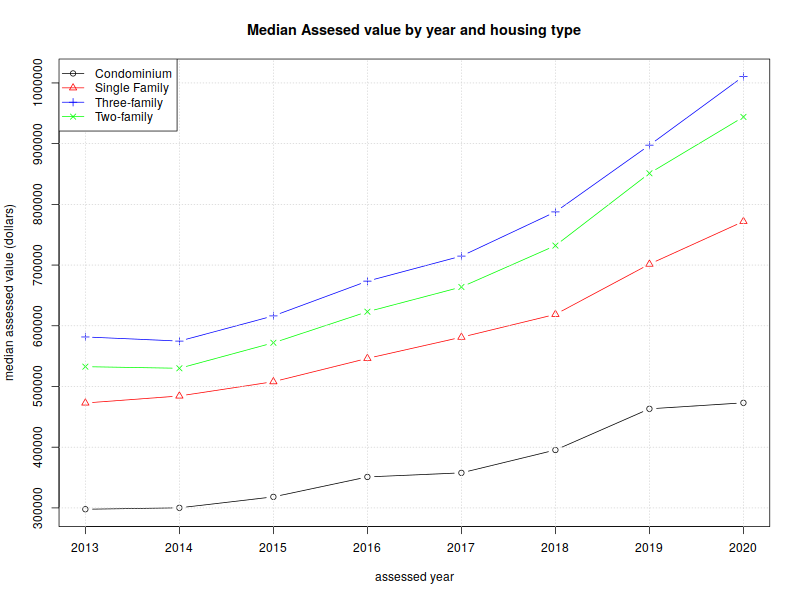
With that background information out of the way, we can look at some numbers. Here’s a graph of the median assessed values for condominiums, one-family, two-family, and three-family homes from 2013 through 2020. (the “median” is a value such that half of the assessments are above, and half are below).
| year | Condominium | Single Family | Two-family | Three-family |
| 2013 | $297,800 | $472,850 | $532,650 | $581,600 |
| 2014 | $300,150 | $484,400 | $530,000 | $574,800 |
| 2015 | $318,200 | $507,900 | $572,000 | $616,300 |
| 2016 | $351,050 | $546,300 | $623,150 | $673,550 |
| 2017 | $357,750 | $581,200 | $663,900 | $714,800 |
| 2018 | $395,400 | $618,800 | $732,100 | $787,600 |
| 2019 | $463,250 | $701,550 | $851,200 | $897,500 |
| 2020 | $473,100 | $771,900 | $944,000 | $1,010,850 |
| %change | 58.87% | 63.24% | 77.23% | 73.81% |
As one would expect, two-family homes are worth more than single-family, and three-family are worth more than two. Condominiums have a lot of variety; they could be half of a duplex, or a single unit in an apartment building. But a general upward trend is clearly evident.
These values are straight out of the assessor’s database, and not adjusted for inflation. The Bureau of Labor Statistic’s inflation calculator shows 12% inflation between 2013 and 2020; the %change is pretty considerable, even if one deducts 12% for inflation.
Next, I’d like to dig further into the 1–3 family assessments, by breaking them down into the value of land vs the value of buildings, and showing how that’s changed over time.
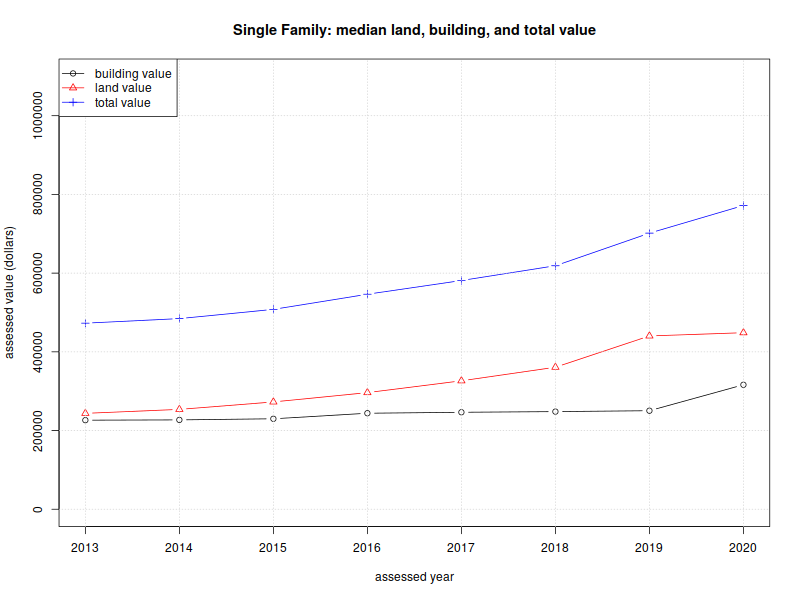
Single-family homes:
| year | Land value | Building value | Total assessed value |
| 2013 | $243,700 | $226,300 | $472,850 |
| 2014 | $253,750 | $227,050 | $484,450 |
| 2015 | $272,700 | $229,900 | $507,900 |
| 2016 | $296,400 | $243,950 | $546,400 |
| 2017 | $326,400 | $246,400 | $581,250 |
| 2018 | $360,900 | $248,100 | $618,800 |
| 2019 | $440,400 | $250,400 | $701,600 |
| 2020 | $448,600 | $316,300 | $771,900 |
| %change | 84.08% | 39.77% | 63.24% |
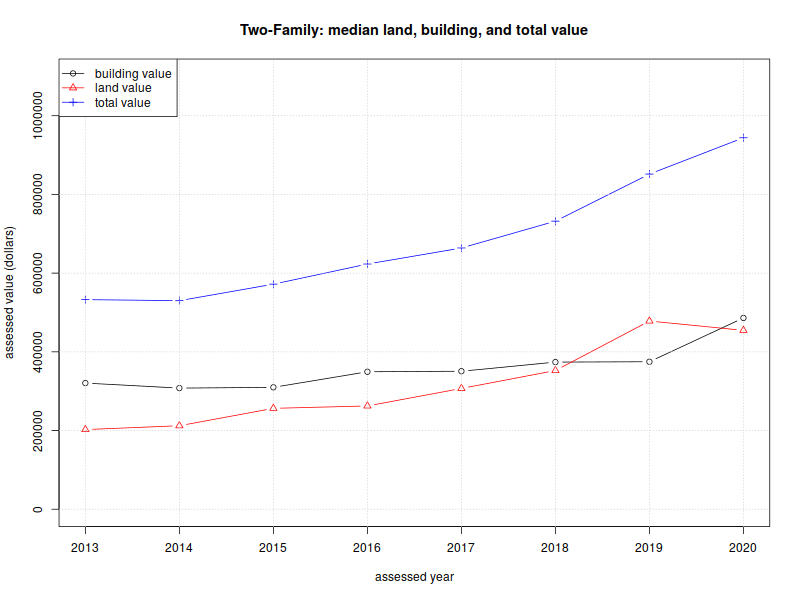
Two-family homes:
| year | Land value | Building value | Total assessed value |
| 2013 | $202,500 | $320,550 | $532,650 |
| 2014 | $212,250 | $307,800 | $530,000 |
| 2015 | $256,400 | $309,800 | $572,000 |
| 2016 | $262,500 | $349,400 | $623,150 |
| 2017 | $307,000 | $350,700 | $663,900 |
| 2018 | $352,500 | $373,900 | $732,100 |
| 2019 | $478,300 | $374,850 | $851,700 |
| 2020 | $454,500 | $486,100 | $944,000 |
| %change | 124.44% | 51.65% | 77.23% |
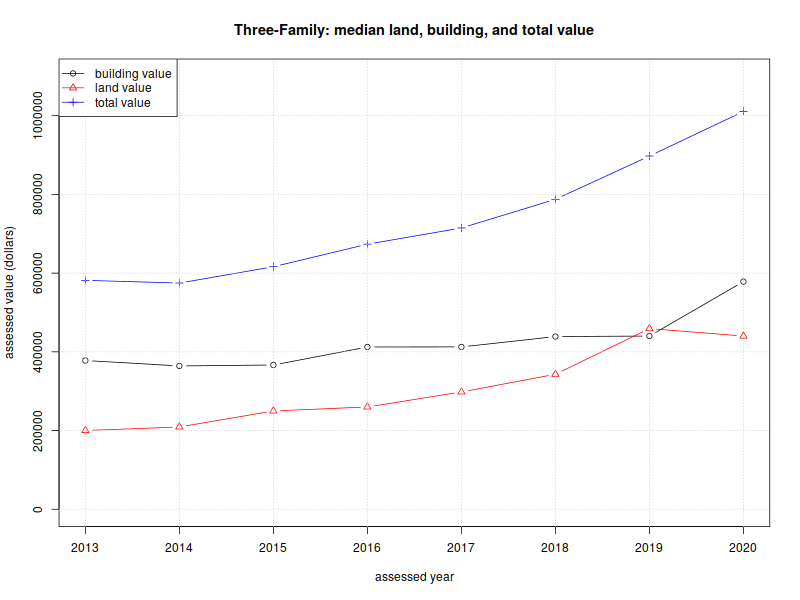
Three-family homes:
| year | Land value | Building value | Total assessed value |
| 2013 | $200,100 | $377,900 | $581,600 |
| 2014 | $209,100 | $364,100 | $574,800 |
| 2015 | $249,800 | $366,550 | $616,300 |
| 2016 | $259,950 | $412,350 | $673,550 |
| 2017 | $298,100 | $412,500 | $714,800 |
| 2018 | $343,050 | $438,800 | $787,600 |
| 2019 | $459,000 | $440,100 | $897,500 |
| 2020 | $440,100 | $578,450 | $1,010,850 |
| %change | 119.94% | 53.07% | 73.81% |
There are several things worth pointing out in these breakdowns.
First, note that the land and building values “jump” a bit between 2019–2020. 2020 was one of our full reassessment years, so I’m willing to attribute this to a periodic course correction. The total increase is generally linear, but the land/building composition has changed.
Second, the median land value for single-family homes is higher than the median building value, for all years between 2013–2020.
Third, most of the increases come from changes in land value. I believe this comes down to location, location, and location. Arlington has a well-respected public school system, and it’s close to universities and tech centers is Cambridge and Boston, and office parks in Lexington, Waltham, and Burlington. City amenities are close at hand.
So what does one do about our rising home prices, and in particular, the rising value of land? The first (and perhaps default) answer is to do nothing. Rising property values are a boon to homeowners who purchased a capital asset (i.e., a house) in the past, and have seen its value appreciate over time. The downside of doing nothing is that each year, increasing housing prices create an ever-increasing income threshold for new residents.
An alternative approach would be to allow more (and smaller) units to be built on each lot. This requires reconstruction or redevelopment, but it allows the cost of land to be amortized among several households. More units/lot means more people and more density, but it reduces the income threshold for buying in to Arlington. (Note that the per-unit cost for three-family homes is lower than the per-unit cost for two-family homes. Similarly, the per-unit cost for two-family homes is lower than the cost of a single-family home).
A third article will look at the distribution of housing prices in Arlington, and how the distribution varies by housing type.
Here is a spreadsheet of data shown in this post.
State Senator Cindy F. Friedman has written a letter to Town Meeting Members supporting Warrant Article 12 and a meaningful MBTA Communities Plan. She writes:
We all want Arlington and Massachusetts to remain welcoming, accessible places to live. In addition to our deficit of housing, I recognize the importance of encouraging smaller, more sustainable housing in walkable areas. Arlington’s Warrant Article 12 will provide a meaningful framework for making progress in these areas. The problems we are experiencing now —out of reach housing prices for new construction and existing homes — exacerbate the crisis and are seriously threatening the economic vibrancy of our communities.
To read Friedman’s full letter, click here for the PDF.
Prepared by: Barbara Thornton with the capable assistance of Alex Bagnall, Pamela Hallett, Patrick Hanlon, Karen Kelleher, Steve Revilak and Jennifer Susse.
As Arlington considers new zoning and other policy decisions to increase the amount of affordable housing in the town, a concern has been raised about the threat of greater costs to the Town’s budget from new people with school age children moving into the town. The concern: additional children in the public schools costs the town more than the additional new property tax revenue the Town collects from the new housing.
This post examines this concern, drawing on data from two recent housing developments, representing 283 units of housing in Arlington, to determine that actually the Town budget gains over 4.5 times the actual cost of paying for the students. According to the most recent 2020 tax bills, the Town expects to collect $1,250,370 in revenue and to spend an additional $269,589 for the new Arlington Public School students living in these developments.
The data suggests that the fear of increased school costs, overwhelming the potential new revenue from new housing construction is not warranted.
For more information, see the full post here.
by Laura Wiener
If you’ve lived in Arlington for a while, your housing costs, whether you rent or own, might be well below what they are for newcomers. Perhaps you, or someone you know is experiencing scary annual rent increases, or would like to buy a house but can’t get near Arlington’s $1 million-plus median price tag.
Arlington, and much of the Commonwealth, has a shortage of housing that is driving up housing prices and increasing homelessness. Renters are particularly hard hit, with median rents over $2500/month. About 1/3 of Arlington’s renters pay more than 30% of their income for housing. In order to get that rent down to something affordable for a low-income household, subsidies are needed. Arlington has been very supportive of building affordable housing, using its CDBG (Federal Community Development Block Grant) and CPA (local Community Preservation Act) funds to that end. It has also worked cooperatively with the Arlington Housing Authority and Housing Corporation of Arlington in support of their affordable housing projects. These subsidy dollars are necessary but not sufficient for building affordable housing.
Land cost is one thing that makes building any housing expensive, and one way to decrease the cost of building affordable housing is to allow more units to be built on a given piece of land. But our zoning limits much of our town to single- and two-family homes on a lot. The Affordable Housing Overlay allows more units to be built on a lot, throughout the Town, and targets those who need it most—low-income households.
A zoning overlay is an alternative set of zoning requirements that can be applied on a piece of land. A builder can choose to build under the alternative Overlay Zoning rules, or under the original zoning, known as the Underlying Zoning. In this case, the proposed Affordable Housing Overlay Zoning can be applied anywhere, on any lot, if at least 70% of the units are priced to be affordable to a household at or below 60% of median income. If 70% of units are affordable, then the structure can be up to 2 stories taller than with the underlying zoning. In addition, any number of units can be built, so long as yard and setback requirements are met. One additional change is that the parking requirement would be a minimum of ½ space per unit. This reflects the actual parking usage at existing affordable housing owned by the Housing Corporation of Arlington. This proposal includes both rental and ownership units that are affordable.
A group of Arlington residents is proposing an amendment to our current zoning to include an Affordable Housing Overlay. This proposal will come before the Redevelopment Board for hearings in winter 2025 (probably during February or March), and then go to Town Meeting in spring 2025. There has already been one informational meeting on November 7 (slides and video), and there may be additional public informational meetings scheduled.
This 102 page document is the most recently revised set of recommendations by the Town of Arlington’s Redevelopment Board. The report takes into consideration the comments and information provided over the last few months’ public hearing process. It also incorporates a citizen petition which strengthens the case for increasing permanent affordable housing with the passage of these zoning related Articles. Town Meeting convenes on April 22, 2019.
You may not know who your Town Meeting Members are. You may not even know what precinct you live in. We’re here to help!
What’s My Precinct?
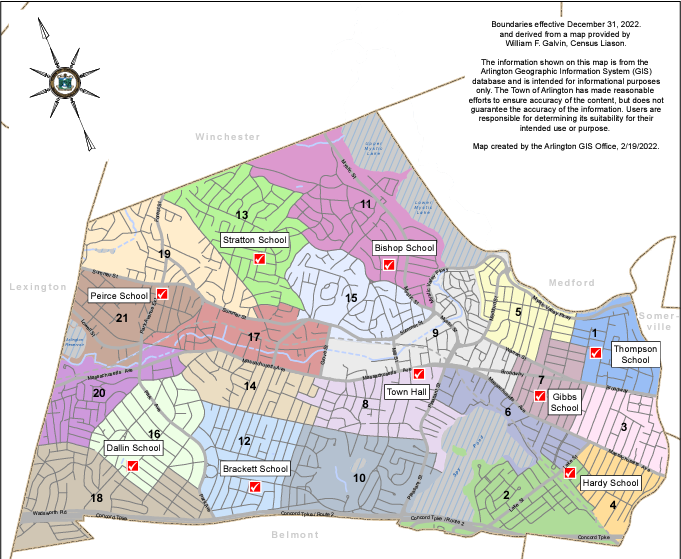
This PDF map of Arlington is divided by precinct. You may need to zoom in to see your precinct.
Who Are My Town Meeting Members?
The town of Arlington has a public list of town meeting members and their contact information. Send them an email telling them how you feel, or ask them if you can take a walk and discuss the MBTA Communities Plan.
Minneapolis is the most recent governmental entity to disrupt the almost 110 year old idea of local zoning in America by overriding single family zoning. Zoning was developed in the the early 1900’s to control property rights and, in part, to limit access to housing by race. These early laws were upheld by the courts in the 1930’s and the use of zoning to control private property for the interests of the majority became common. Houston Texas did not adopt zoning, an outlier in the nation.
But recently governments are rethinking zoning in light of evidence of exclusionary practices including racism and inadequate supplies of affordable housing. In July Oregon’s legislature voted to essentially ban single family zoning in the state.
Most recently, in the end of July, Minneapolis became the first city this century to remove single family zoning, allowing two family housing units to enter any single family zone as of right. According to the Bloomberg News article, the city took action to remedy the untenable price increases do to single family homes taking a disproportionate amount of city land and services. They hope a wider range of housing, and more housing, will reduce housing costs in the future.
Read the full story from Bloomberg News.
It’s New Year’s eve and I’m determined to get my third and final “Arlington 2020” article written and posted before 2021 rolls in. I’ve written these articles to paint a picture of Arlington’s housing stock, and how our housing costs have changed over time. The first article looked at the number of one-, two-, and three-family homes and condominiums in Arlington. The second article looked at how the costs of these homes has varied over time.
In this article, I’m going to look at the per-unit costs for our different housing types. The per-unit cost is just the assessed value, divided by the number of units. For condos and single-family homes, the unit cost is simply the assessed value. For two-family homes, it’s the assessed value divided by two. For a ten-unit apartment building, it’s the assessed value divided by ten. We’ll look at the price ranges within housing types, as well as the general differences between them.
The information here doesn’t include residential units from Arlington’s 76 mixed-use buildings. (My copy of the assessor’s data doesn’t distinguish between residential and commercial units in these buildings; I’ll try to say more about them in 2021.) It also omits units owned by the Arlington Housing Authority.
Condominiums
Condominiums provide the most variety and cost diversity. A condo can be half of a duplex, or part of a much larger multi-family building. The low end of the scale tends to be 500–600 square foot units that were built in the 1960’s; the high end tends to be more spacious new construction.
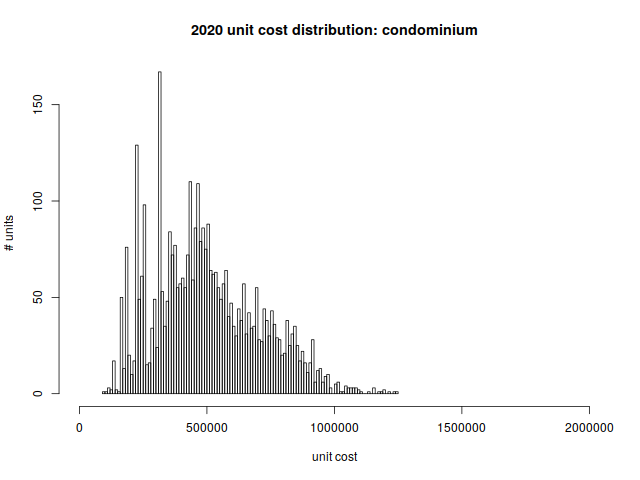
This graph is a histogram, as are the others in this article. The horizontal axis shows cost per unit, and the vertical axis shows the number of units in each particular cost band.
The per-unit price distribution is
| min | 1st quartile | median | mean | 3rd quartile | max |
| $92,600 | $344,450 | $473,100 | $500,086 | $640,850 | $1,241,000 |
Single-family homes
Single family homes are heavily concentrated around the $700,000 mark. There’s very little available for less than a half million dollars.
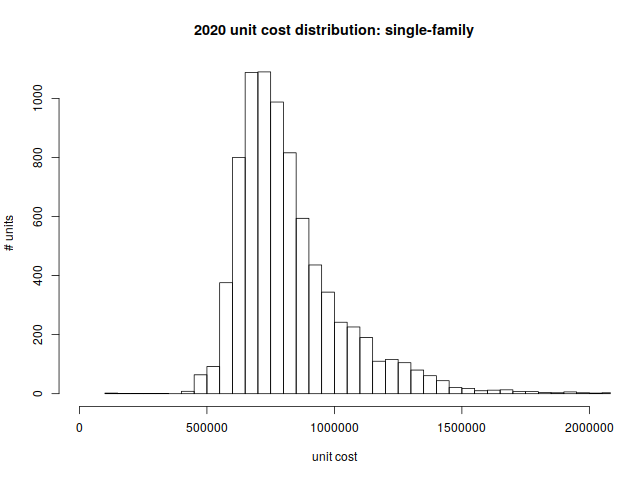
Per unit rice distribution:
| min | 1st quartile | median | mean | 3rd quartile | max |
| $103,700 | $679,900 | $771,900 | $825,172 | $908,750 | $3,232,700 |
The $103,700 single-family home deserves some explanation. The property straddles the border between Arlington and Lexington; it appears that the $103k assessed value reflects the portion that lies in Arlington.
Two-family Homes
Two-family homes are the bread and butter of East Arlington; they’re also common in the blocks off Mass ave near Brattle Square and the heights. Many of these homes are older and non-conforming, and they’re gradually being renovated and turned into condominiums.
As a reminder, these are costs per unit (as opposed to the cost of the entire two-family home).
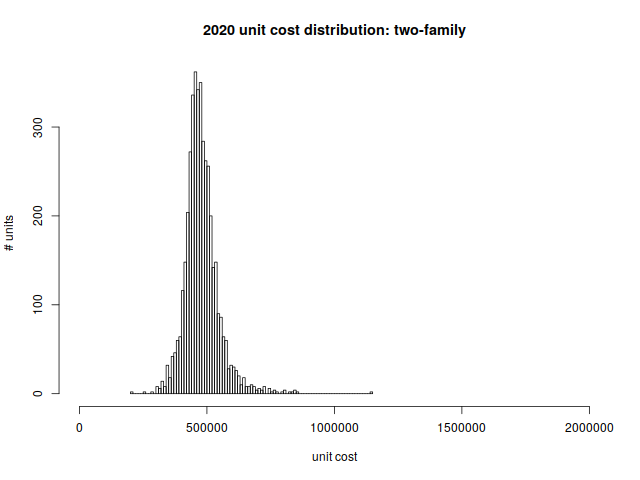
Per unit price distribution:
| Min | 1st quartile | median | mean | 3rd quartile | max |
| $209,050 | $440,550 | $472,000 | $479,175 | $508,588 | $1,140,450 |
Three-family Homes
Unlike Dorchester and Somerville, three-family homes are not a staple of Arlington’s housing stock. But we have a few of them. Most were built between 1906 and 1930.
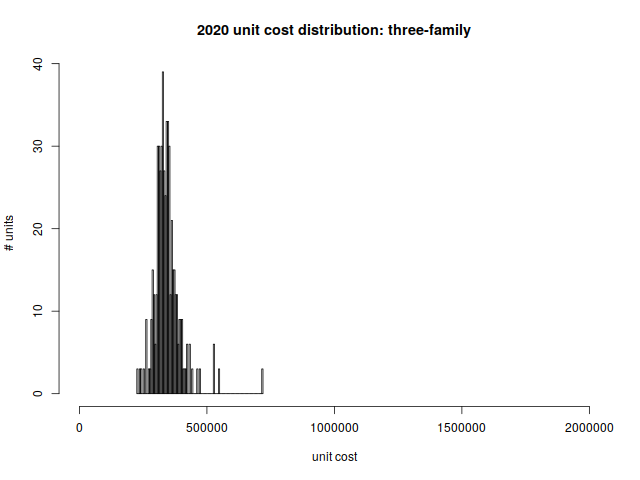
Per-unit price distribution:
| Min | 1st quartile | median | mean | 3rd quartile | max |
| $227,567 | $313,733 | $336,950 | $344,292 | $362,600 | $719,000 |
Small Apartments (4–8 units)
The majority of Arlington’s small apartment buildings were constructed during the first half of the 20th century. The most recent one dates from 1976.
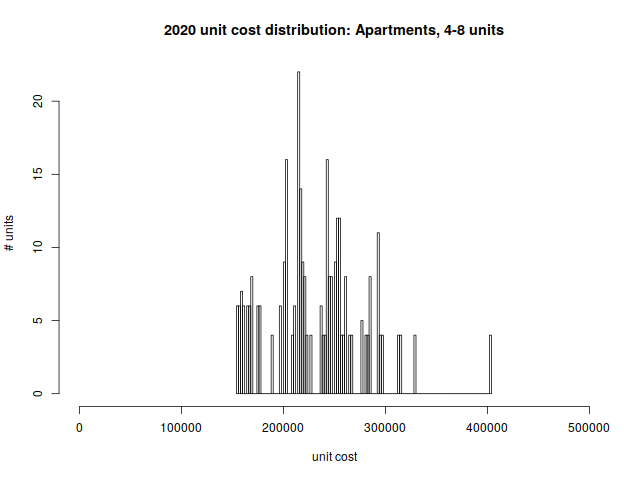
Per-unit price distribution:
| Min | 1st quartile | median | mean | 3rd quartile | max |
| $154,950 | $202,950 | $227,775 | $231,619 | $255,775 | $403,875 |
Large Apartments (9+ units)
You’ll see three outliers in the per unit-cost distribution for large apartment buildings. These correspond to the newest apartment complexes in Arlington: The Legacy (2000), Brigham Square (2012), and Arlington 360 (2013).
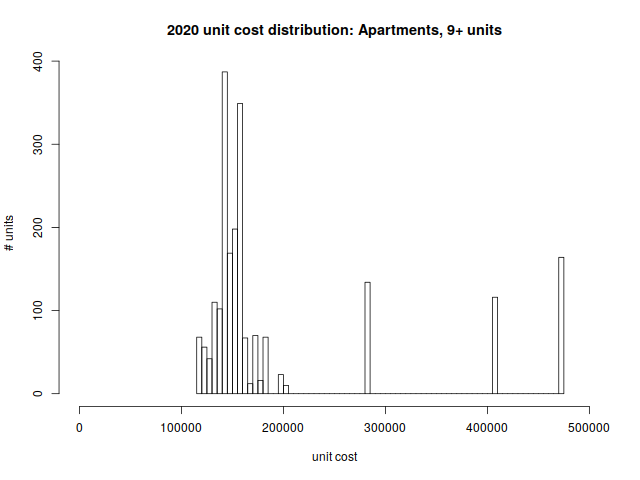
Per-unit price distribution:
| Min | 1st quartile | median | mean | 3rd quartile | max |
| $117,013 | $141,383 | $153,006 | $195,789 | $170,973 | $474,631 |
All combined
Finally, we’ll put it all together in one picture, representing nineteen-thousand and some odd homes in town.
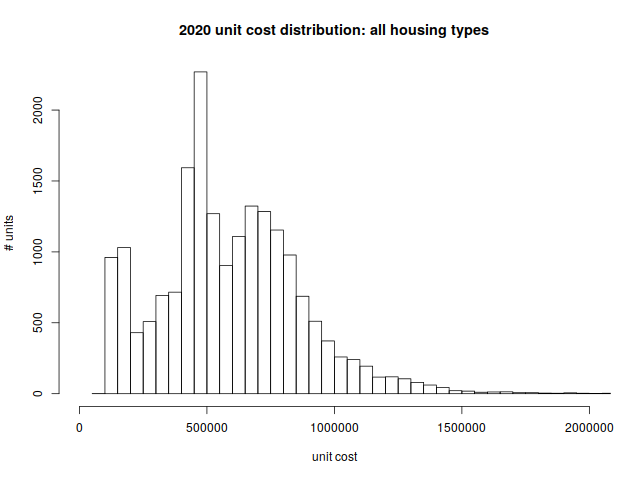
Per-unit price distribution:
| Min | 1st quartile | median | mean | 3rd quartile | max |
| $92,600 | $417,175 | $555,825 | $587,975 | $759,900 | $3,232,700 |
While there are lower-priced options available, a person coming to Arlington should expect to buy (or rent) a property that costs just shy of half a million dollars (or more).
Here is a spreadsheet with the cost distributions mentioned in this article.
