The citizen participation process including presentations, discussions, public hearings, letters and comments has been long and arduous. The issues are complicated and sometimes feelings run high. In such situations, there can be a feeling that citizens have not been heard. This document, “Guide to Zoning Amendments Related to Multifamily Uses and Mixed-Use“, summarizes many of the issues that have been raised and the changes that have been made in the zoning Articles as a result of the citizen participation in the public review process. Citizens have been heard.
Related articles
Dave Weinstock, an Arlington resident interested in affordable housing wondered about the concept of “developer math”. The math involved in planning an affordable housing projects is a problem that needs to get solved in order to have anything built here in Arlington, or anywhere. This topic comes up frequently in community discussions about the need for more housing.
Questions are raised around:
- 1- Why build so many units vs. smaller buildings
- 2- Why parking is costly and inefficient use of land
- 3- Why can’t more affordable or all affordable units be built?
- 4- The cost of subsidizing affordable units and how that may translate to higher rental rates/costs, etc.
Dave found a great Architecture and Development firm in Atlanta (Kronberg Urbanists + Architects, based in Atlanta GA) that lays out a nice presentation, includes sample proformas, and real life scenarios that may help us understand this piece of the puzzle better when evaluating any project and how developers may be incented to build certain types of projects or do certain types of work.
Here is a link, reformatted to be within this website, to the presentation, showing the varieties of choices, costs, formulas and outcomes developers consider before deciding if the project can be built: https://equitable-arlington.org/developer-math_kua_071420/
Much of our hope for more affordable housing depends on the market forces of capitalism and the willingness of developers to build for good, not just for profit. But the developers must be able to cover their costs. Many communities are highly skeptical of developers, assuming the community will get tricked, the developer will get greedy and the promised housing will be a disappointment. Trust is needed. But so is verification. We all need to learn the developer math.
What are the math factors that a developer considers before deciding to build affordable housing?
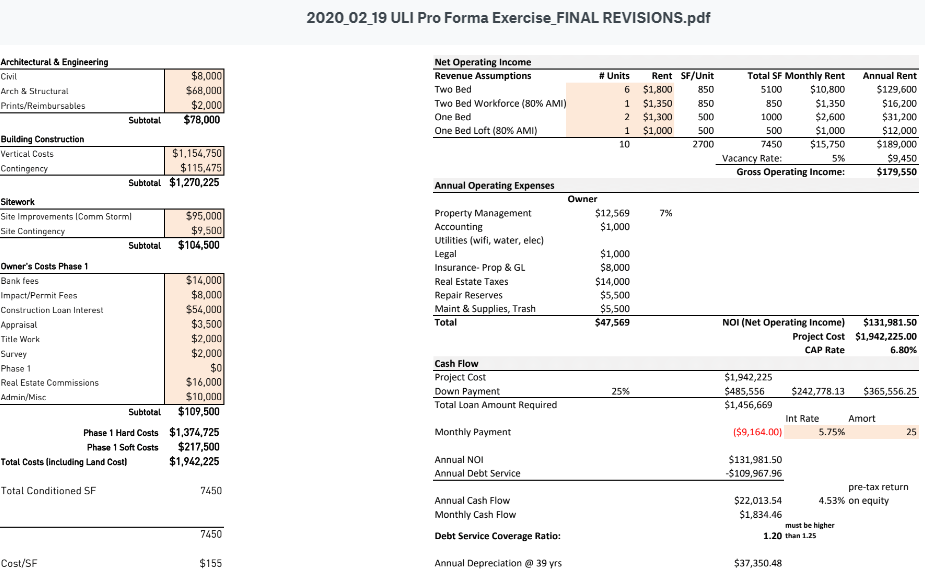
Here is a link to the original presentation. https://www.kronbergua.com/post/mr-mu-let-s-talk-about-math
The new proposal is just the most recent step in a process that reaches back almost a decade, culminating in the Master Plan (2015), the Housing Production Plan (2016) and the mixed-using zoning amendments of 2016. The Town has consistently proposed smart growth: more development along Arlington’s transit corridors to increase the tax base, stimulate local commerce, and provide more varied housing opportunities for everyone, including low and moderate income Arlingtonians. This year’s proposals are no head-long rush into change. Today’s debate is similar to the debate before Town Meeting three years ago. If anything, progress has been frustratingly slow. To realize the Master Plan’s vision of a vibrant Arlington with diverse housing types for a diverse population, we must stay the course on which we have been embarked for so long.
Article 1 in a series on the Arlington, MA master planning process. Prepared by Barbara Thornton
Arlington, located about 15 miles north west of Boston, is now developing a master plan that will reflect the visions and expectations of the community and will provide enabling steps for the community to move toward this vision over the next decade or two. Initial studies have been done, public meetings have been held. The Town will begin in January 2015 to pull together the vision for its future as written in a new Master Plan.
In developing a new master plan, the Town of Arlington follows in the footsteps laid down thousands of years ago when Greeks, Romans and other civilizations determined the best layout for a city before they started to build. In more recent times, William Penn laid out his utopian view of Philadelphia with a gridiron street pattern and public squares in 1682. Major Pierre Charles L’Enfant developed the hub and spoke street plan for Washington DC in 1798. City planning started with new cities, relatively empty land and a “master builder” typically an architect, engineer or landscape architect commissioned by the land holders to develop a visionary design.
In the 1900’s era of Progressive government in America, citizens sought ways to reach a consensus on how their existing cities should evolve. State and federal laws passed to help guide this process, seeing land use decisions as more than just a private landowner’s right but rather a process that involved improving the health and wellbeing of the entire community. While the focus on master planning was and still is primarily physical, 21st century master planners are typically convened by the local municipality, work with the help of trained planners and architects and rely heavily on the knowledge and participation of their citizenry to reflect a future vision of the health and wellbeing of the community. This vision is crafted into a Master Plan. In Arlington the process is guided by Carol Kowalski, Director of Planning and Community Development, with professional support from RKG Associates, a company of planners and architects and with the vision of the Master Planning advisory committee, co-chaired by Carol Svenson and Charles Kalauskas, Arlington residents, and by the citizens who share their concerns and hopes with the process as it evolves. This happens through public meetings, letters, email, and surveys. The most recent survey asks residents to respond on transportation modes and commuting patterns
We all do planning. Starting a family, a business or a career, we lay out our goals and assume the steps necessary to accomplish these goals and we periodically revise them as necessary. The same thing is true for cities. Based on changes in population, economic development, etc. cities, from time to time, need to revise their plans. In Massachusetts the enabling acts for planning and zoning are here http://www.mass.gov/hed/community/planning/zoning-resources.html. The specific law for Massachusetts is MGL Ch. 41 sect. 81D. This plan, whether called a city plan, master plan, general plan, comprehensive plan or development plan, has some constant characteristics independent of the specific municipality: focus on the built environment, long range view (10-20 years), covers the entire municipality, reflects the municipality’s vision of its future, and how this future is to be achieved. Typically it is broken out into a number of chapters or “elements” reflecting the situation as it is, the data showing the potential opportunities and concerns and recommendations for how to maximize the desired opportunities and minimize the concerns for each element.
Since beginning the master planning process in October, 2012, Arlington has had a number of community meetings (see http://vod.acmi.tv/category/government/arlingtons-master-plan/ ) gathering ideas from citizens, sharing data collected by planners and architects and moving toward a sense of what the future of Arlington should look like. The major elements of Arlington’s plan include these elements:
1. Visions and Goals http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19829
2. Demographic Characteristics http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19838
3. Land Use http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19834
Working paper: http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19825
4. Transportation http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19830
Working paper: http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19822
5. Economic Development http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19837
Working paper: http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19828
6. Housing http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19835
Working paper: http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19826
7. Open Space and Recreation http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19832
Working paper: http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19824
8. Historic and Cultural Resources http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19836
Working paper: http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19827
9. Public Facilities and Services http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19831
Working paper: http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19823
10. Natural Resources
Working paper: http://www.arlingtonma.gov/home/showdocument?id=19824
The upcoming articles in this series will focus on each individual element in the Town of Arlington’s Master Plan.
This letter appeared in the Boston Globe on Dec. 19th. It’s reprinted
here with permission from the author, Eugene Benson.
The Dec. 12 letter from Jo Anne Preston unfortunately repeats misinformation making the rounds in Arlington (“Arlington is a case study in grappling with rezoning“).
At April Town Meeting, the Arlington Redevelopment Board recommended a vote of no action on its warrant article that would have allowed increased density along the town’s commercial corridors in exchange for building more affordable housing (known as “incentive zoning”), when it became obvious that the article would be unlikely to gain a two-thirds vote for passage, in part because of the complexity of what was proposed.
A warrant article to allow accessory dwelling units in existing housing (“in-law apartments”) gained more than 60 percent of the vote at Town Meeting but not the two-thirds vote necessary to change zoning.
The letter writer mentioned “naturally occurring affordable apartment buildings.” The typical monthly rent for an apartment in those older buildings ranges from about $1,700 for a one-bedroom to about $2,300 for a two-bedroom, according to real estate data from CoStar. Those are not affordable rents for lower-income people. For example, a senior couple with the national average Social Security income of about $2,500 per month would spend most of their income just to pay the rent.
We need to protect the ability of people with lower incomes to withstand rent increases and gentrification. That, however, requires a different approach than hoping for naturally occurring affordable housing to be there even five years from now.
Eugene B. Benson
Arlington
The writer’s views expressed here are his own, and are not offered on behalf of the Arlington Redevelopment Board, of which he is a member.
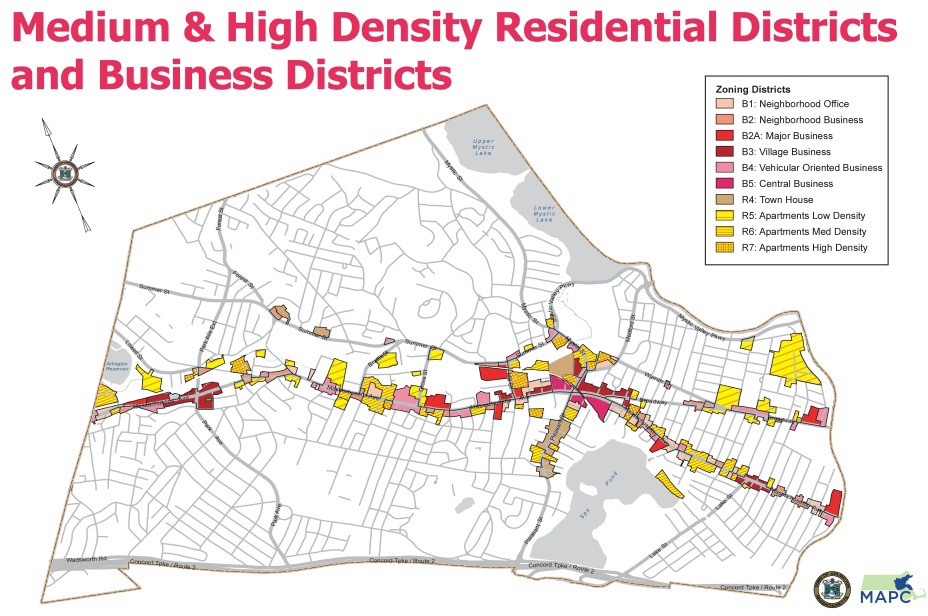
The discussions on zoning have been confusing because while zoning covers ALL of Arlington’s land and the zoning bylaws for all Arlington’s zones are referenced, the key issues of greatest interest to Town Meeting are the discussions about increasing density. These discussions pertain ONLY to those properties currently zoned as R4-R7 and the B (Business) districts. These density related changes would affect only about 7% of Arlington’s land area. The map shows the specific zones that would potentially be affected. They lay along major transportation corridors.
During the last few months, Arlington’s Department of Planning and Community Development and Zoning Bylaw Working Group have been conducting a study of the town’s industrial districts. The general idea has been to begin with an assessment of current conditions, and consider whether there are zoning changes that might make these districts more beneficial to the community as a whole.
To date, the major work products of this effort have been:
- A study of existing conditions, market analysis, and fiscal impact. Among other things, this slide deck will show you exactly where Arlington’s industrial districts are located.
- A set of test build scenarios.
- An initial set of zoning recommendations. These are high level ideas; they’d need further refinement to fit into the context of our zoning bylaws.
- A survey, to gather public input on several of the high-level recommendations.
The survey recently closed. I asked the planning department for a copy of they survey data, which they were generous enough to provide. That data is the subject of this blog post.
The survey generally consisted of pairs of questions: a yes/no or multiple choice, coupled with space for free-form comments. I’ll provide the yes/no and multiple choice questions (and answers!) here. Those interested in free-form commentary can find that in the spreadsheet linked at the bottom of this article.
208 people responded to the survey.
Industrial Zoning questions
(1) Which of the following uses would you support in the Industrial Districts? (check all that apply) (208 respondents)
| Industrial | 62.02% |
| Office | 76.92% |
| Breweries, Distilleries, and Wineries | 86.06% |
| Mixed Use (Office and Industrial Only) | 67.31% |
| Food Production Facilities | 55.77% |
| Flexible Office/Industrial Buildings | 68.27% |
| Coworking Space | 68.75% |
| Maker Space | 63.46% |
| Vertical Farming | 65.38% |
| Work Only Artist Studio | 63.94% |
| Residential | 42.79% |
| Other (please specify) | 12.02% |
(2) Would you support a waiver of the current 39-foot height maximum to allow heights up to 52 feet if the Applicant had to meet other site design, parking, or environmental standards? (207 respondents)
| Yes | 74.40% |
| No | 22.22% |
(3) Would you support a small reduction in the amount of required parking by development as an incentive to provide more bike parking given the districts’ proximity to the Minuteman Bikeway? (208 respondents)
| Yes | 68.27% |
| No | 30.77% |
(4) Would you support a variable front setback of no less than 6 feet and no more than 10 feet to bring buildings closer to the sidewalk and create a more active pedestrian environment? (207 respondents)
| Yes | 66.18% |
| No | 28.50% |
(5) Would you support zoning changes that require new buildings in the district to have more windows and greater building transparency, as well as more pedestrian amenities such as lighting, landscaping, art, or seating? (207 respondents)
| Yes | 81.64% |
| No | 13.53% |
Demographic questions
(7) Do you….(check all that apply) (206 respondents)
| live in Arlington | 99.51% |
| work in Arlington | 23.79% |
| own a business in Arlington | 9.71% |
| work at a business in one of Arlington’s industrial districts | 1.46% |
| own a business in one of Arlington’s industrial districts | 1.46% |
| patron of Arlington retail and restaurants | 76.70% |
| elected official in Arlington | 6.80% |
(8) What neighborhood do you live in? (207 respondents)
| Arlington Heights | 30.43% |
| Little Scotland | 2.42% |
| Poet’s Corner | 0.97% |
| Robbins Farm | 5.80% |
| Turkey Hill/ Mount Gilboa | 11.11% |
| Morningside | 4.35% |
| Arlington Center | 10.14% |
| Jason Heights | 8.21% |
| East Arlington | 20.77% |
| Kelwyn Manor | 0.00% |
| Not Applicable | 0.48% |
(9) How long have you lived in Arlington? (207 respondents)
| Under 5 years | 19.32% |
| 5 to 10 years | 15.46% |
| 10 to 20 years | 19.81% |
| Over 20 years | 45.41% |
According to US Census data [1], 72% of Arlington’s residents moved to Arlington since the beginning of the 2000’s (i.e., 20 years ago or less). The largest group responding to this survey has lived here 20+ years, implying that the results may be more reflective of long-term residents opinions.
(10) Please select your age group (199 respondents)
| Under 18 | 0.00% |
| 18-25 | 1.01% |
| 26-35 | 13.57% |
| 36-45 | 22.11% |
| 46-55 | 25.13% |
| 56-65 | 20.60% |
| 66-80 | 16.58% |
| 80+ | 1.01% |
(11) What is your annual household income? (188 respondents)
| $0-$19,999 | 1.06% |
| $20,000-$39,999 | 1.60% |
| $40,000-$59,999 | 5.32% |
| $60,000-$79,999 | 9.04% |
| $80,000-$99,999 | 4.79% |
| $100,000-$149,999 | 23.94% |
| $150,000-$200,000 | 17.55% |
| More than $200,000 | 36.70% |
Full Survey Results
As noted earlier, the survey provided ample opportunity for free-form comments, which are included in the spreadsheet below. There were a number of really thoughtful ideas, so these are worth a look.
Arlington Industrial District Survey
Footnotes
[1] https://censusreporter.org/profiles/16000US2501640-arlington-ma/, retrieved August 10th, 2020
Many issues are under discussion as a result of these proposed zoning Articles. Issues include: housing affordability, the diversity of housing and incomes in Arlington, environmental concerns and sustainability, tax burdens or tax savings potentially resulting from growth, the risk of postponing the decisions, and the image of Arlington as a community that values diversity and equitability. This one page “fact sheet” attempts to address many of these issues and concerns.
(This post was originally an email message, discussion open space changes proposed by an Affordable Housing article during the Arlington, MA’s 2019 town meeting. It’s also a decent description of our town’s open space laws.)
Sorry this turned out to be a long post. Our open space laws are kind of complicated.
Arlington regulates open space as a percentage of gross floor area, rather than as a percentage of lot area. Let me give a concrete example: say we have a-one story structure with no basement. It covers a certain percentage of the lot area, and has an open space requirement based on the gross floor area (i.e., the interior square footage of the building).
Now, suppose we want to turn this into a two- or three-story structure. The building footprint does not change, and it covers exactly the same percentage of the lot area. However, the open space requirements double (if you’re doing a two-story building), or triple (if you’re doing a three story building). If that quantity of open space isn’t on the lot, then you can’t add the stories.
For this reason, I’d argue that our open space regulations are primarily oriented to limiting the size of buildings. You really can’t allow more density (or taller buildings) without reducing the open space requirements. Alternatively, if the requirements were based on a percentage of lot area, we probably wouldn’t need a reduction. (Cambridge’s equivalent is “Private Open Space”, and they regulate it as a percentage of lot area.)
The other weird thing about our open space laws is that we define “usable open space” in such a way that it’s possible to have none. (Usable open space must have a minimum horizontal dimension of 25′, a grade of 8% or less, and be free of parking and vehicular traffic). I live on a nonconforming lot that does not meet these requirements, as do the majority of homes in my neighborhood.
Suppose I wanted to build an addition, which would increase the gross floor area. With the non-conformity, I’d have to go in front of the ZBA and show that the current lot has 0% usable open space, and that the house + addition produces a lot with 0% usable open space. Because 0% = 0%, I have not increased the nonconformity, and would be able to build the addition, provided that all of the other dimensional constraints of the bylaw are satisified. Although this isn’t directly related to Article 16, it’s an amusing side effect of how the bylaw is written.
Finally, roofs and balconies. Section 5.3.19 of our current ZBL allows usable open space on balconies at least six feet wide, and on roofs that are no more than 10′ above the lowest occupied floor. We allow 50% of usable open space requirements to be satisfied in this manner.
The relevant section of Article 16 would create a 8.2.4(C)(1) which includes the language
Up to 25% of the landscaped open space may include balconies at least 5 feet by 8 feet in size only accessible through a dwelling unit and developed for the use of the occupant of such dwelling unit.
Article 16’s incentive bonuses strike the usable open space requirement, and double the landscaped open space requirement. With only landscaped open space, 5.3.19 doesn’t apply (it only pertains to usable open space). The language I’ve quoted adds something 5.3.19-like, but for landscaped open space. I say 5.3.19-like because it has a 25% cap rather than a 50% cap, and requires eligible balconies to be at least 5’x8′, rather than 6′ wide.
Here are a few pieces of supporting documentation:
- definitions of landscaped and usable open space from our ZBL
- a diagram to illustrate the difference between landscaped and usable open space.
- The text of section 5.3.19 (which is referenced by the diagram)
- the main motion for Article 16